ON-LINE ANALYZERS
Analysis of Calcium and Magnesium in Purified Brine
Purpose
Calcium and magnesium, and to a lesser extent strontium and barium are toxic for the electrolyzer membranes. Poisoning of the membranes results in higher electrolyzer power consumption and is irreversible. Good plant operation practices and the regular testing of the calcium and magnesium by a manual method is usually enough to run the plant in good conditions. However, the manual method is rather slow, and results come several hours apart. An automatic analyzer gives analysis results every 5 to 10 minutes.
Benefits
Cost Reduction
Closely adjust the period of regeneration of the ion-exchange resin columns, therefore reducing the amount of regeneration chemicals consumed.
Closely adjust the period of regeneration of the ion-exchange resin columns, therefore reducing the amount of regeneration chemicals consumed.
Prevention
Immediately warning the operators of any accidental surge in calcium and magnesium concentration due, for example, to premature saturation of the resin of one column, or to breakthrough of filtered brine through the resin bed.
Immediately warning the operators of any accidental surge in calcium and magnesium concentration due, for example, to premature saturation of the resin of one column, or to breakthrough of filtered brine through the resin bed.
Rapid Amortization
The Calcium Magnesium analyzer for pure brine is amortized in less than one year.
The Calcium Magnesium analyzer for pure brine is amortized in less than one year.
Implementation
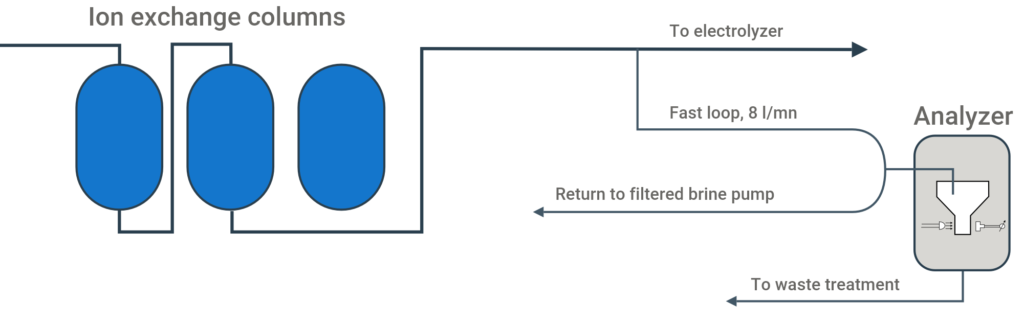
Analytical Method
This analyzer uses the colorimetric method based on “Standard Methods 3500-Ca”. HNB colour indicator is added to the brine sample. Reaction with available calcium or magnesium ions produces a blue colour, that absorbs light at a wavelength of 610 nm. The absorbtion is measured. Then EDTA is added, that captures the calcium and magnesium ion. The HNB becomes red and the absorption changes. The change in absorption provide an accurate measurement of the quantity of calcium and magnesium present in the sample.
The absorption is measured several times at different steps of the process, to detect possible situation where the method will produce invalid readings. For example, if there is a very high concentration of calcium (ppm) due to a breakthrough of filtered brine through the ion exchange beds, or an absence of sample or strange NaCl concentration, or invalid or run-out of reagents.
Analysis Sequence
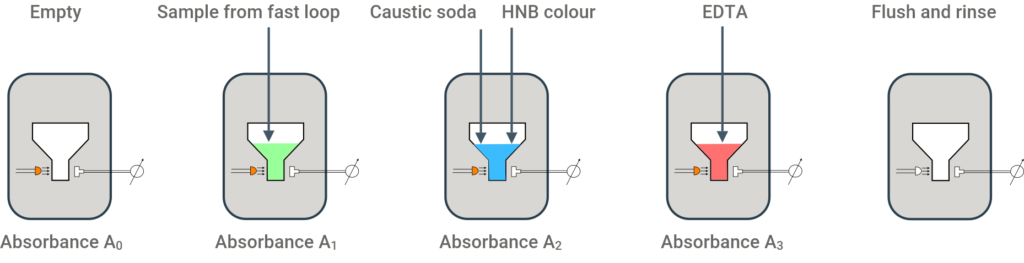
Measurements A0 an A1 are for process checks. The difference between A3 and A2 provides the calcium and magnasium concentration.
Specifications
| Expected brine sample concentration | 300 g/l to 320 g/l NaCL |
| Sample fast loop flow rate | 6 L/mn |
| Quantity measured | Calcium + magnesium |
| Range | 1 ppb to 100 ppb |
| Detection limit | 1 ppb |
| Duration of the analysis | 5 min |
| Precision | 2% |
| Repeatability | below 1% |
Calibration method
The calibration method is incremental and automatic, using a drop by drop addition of a 1 ppm calcium chloride solution to determine the gain factor.
Reagents used
- Colored indicator: Hydroxynaphtol Blue
- pH adjustment solution: Caustic soda
- EDTA solution
- Calibration solution: Calcium chloride
Requirements / Usage conditions
- Ambiant temperature 10°C – 40°C
- Designed for use under shelter (IP65)
- Power required 230V AC, 5 Amps
Outputs
| Concentration (Calcium + Magnesium) | 4 -20 mA |
| Available alarms (potential free contacts) | Ca+Mg concentration exceed a preset alarm value |
| Ca+Mg too high to measure | |
| Brine NaCl concentration too low or no sample | |
| Reagent run-out | |
| Colorimeter fault | |
| Temperature out of control | |
| MODBUS communication | |
| Screen display | |
Get in touch with us now to get a quotation.
Our engineers will help you to conceptualize, size, source the best equipment and deliver the solutions that will fulfill your needs.
The solution your looking for is not listed here? Feel free to contact us anyway!
We keep developing new ideas.